Description
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example
Example 1
1 | Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 |
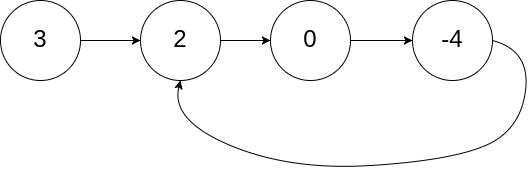
Example 2
1 | Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0 |
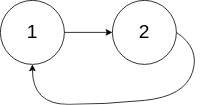
Example 3
1 | Input: head = [1], pos = -1 |

Interface
1 | /** |
Solution
使用 stl::map
map<ListNode*, int> 将 ListNode* 与 ListNode* 出现的次数进行对应,如果单链表中不存在环则,则遍历到尾结点的 next 指向的 nullptr 时就会结束遍历,返回 nullptr;而如果单链表中存在环,第一个出现次数大于 1 的结点即环的入口结点。
1 | /** |
使用 stl::set
与使用 stl::map 的思路相似,故不再叙述。
1 | /** |
Improvement
使用快慢指针
设定两个指针,一个慢指针,一个快指针,慢指针一次走的距离是一个结点,而快指针一次走的距离是两个结点,即快指针的速度是慢指针的两倍。
此时,会出现两种情况:
单链表中不存在环则:快指针往后遍历的过程中,会遍历到 nullptr 结点,即单链表中不存在环,最后一个结点指向的是 nullptr。
单链表中存在环则:由于存在环,则快慢指针最后都会进入环中并在环中一直循环,由于快慢指针存在速度差,只要快慢指针一直在环中循环,最终会在环中的一个结点相遇,相遇时快指针至少在环中循环了一圈。
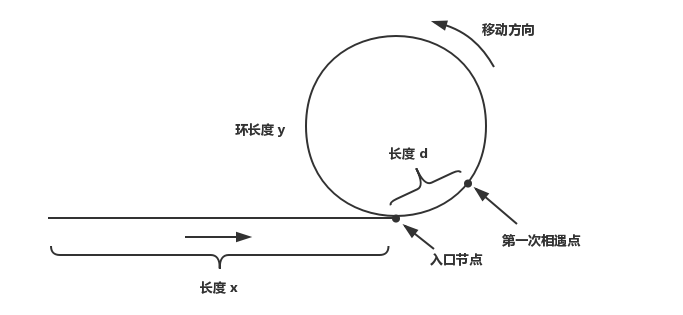
如果这时快指针已经是在环里走了 1 圈(对应于非环部分较短的情况):
此时快指针走了 2(x + d) (0 <= d) 距离,2(x + d) = x + y + d ,可得 x = y - d ,此时再同时从第一次相遇点和头结点出发,速度都为一个结点每次,最后两指针会在环入口结点处相遇。
如果这时快指针已经是在环里走了不止一圈,假设为 k 圈:
此时快指针走了 2(x + d) (0 <= d) 距离,2(x + d) = x +ky + d,可得 x = ky - d ,此时再同时从第一次相遇点和头结点出发,速度都为一个结点每次,最后两指针也会在环入口结点处相遇。
1 | /** |
详细思路参考:一个链表中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点
